29 April 2010
Aquinas on privation
As was said above (A[1]), evil imports the absence of good. But not every absence of good is evil. For absence of good can be taken in a privative and in a negative sense. Absence of good, taken negatively, is not evil; otherwise, it would follow that what does not exist is evil, and also that everything would be evil, through not having the good belonging to something else; for instance, a man would be evil who had not the swiftness of the roe, or the strength of a lion. But the absence of good, taken in a privative sense, is an evil; as, for instance, the privation of sight is called blindness. Now, the subject of privation and of form is one and the same---viz. being in potentiality, whether it be being in absolute potentiality, as primary matter, which is the subject of the substantial form, and of privation of the opposite form; or whether it be being in relative potentiality, and absolute actuality, as in the case of a transparent body, which is the subject both of darkness and light. It is, however, manifest that the form which makes a thing actual is a perfection and a good; and thus every actual being is a good; and likewise every potential being, as such, is a good, as having a relation to good. For as it has being in potentiality, so has it goodness in potentiality. Therefore, the subject of evil is good.
08 April 2010
NY Times Patient Voices series
Here're some of the pain related ones:
Patient Voices: Rheumatoid Arthritis
01 April 2010
Review of David Biro's The Language of Pain

Short story: David Biro's The Language of Pain: Finding Words, Compassion and Relief is very good.
Go buy it.
Longer story: The publisher sent me an advance copy of Biro's The Language of Pain a few months ago. I've read it several times and been working on a review to share with y'all. But the review is getting too long and though I think I agree with most of his conclusions, I'm still not entirely sure what I think about about several of his arguments. Nonetheless, I've certainly profited from engaging with them.
Thus in the interest of posting something while the book is still (somewhat) fresh, I've pasted some of the early parts of the review below. I may post the rest later, or I may work it into something for a more formal venue. I'm omitting the philosophical discussion of the arguments. Though I will list a couple of the topics that concern me. I'm sure the list won't make sense until you've read the book. But perhaps they'll serve as discussion-starters
----
Those interested in learning about pain can profit from David Biro’s The Language of Pain: Finding Words, Compassion and Relief. It will probably be the most useful to people with chronic pain and those close to them. At the very least, the vast array of nuanced metaphors and literary sources he canvases can serve as raw material for their attempts to communicate and understand the experience of pain. But I expect that his lucid exploration of the structure of these metaphors will provide important conceptual tools for crafting more systematic and effective narratives. Though the applicability of some of his particular insights may be limited by culture and language.
Clinicians and scientists should be impressed by the conceptual structure that Biro uncovers in the language many sufferer's use to describe their pains. He succeeds in showing that this metaphorical talk, while necessarily imprecise and often obscure, must be taken seriously. In his wake, the same cannot be said for those who dismiss or deride these ways of talking about pain.
At a minimum, researchers interested in developing pain measurement tools and many philosophers will find in it a rich repository of examples and ideas to use in their work.
Philosophers should also find much to be intrigued by in Biro’s arguments. Here are a few of points that I think are worth engaging with:
- Chapter 2 is occupied with a theoretical response to the charge that pain is completely resistant to language. This is unnecessary. The main thrust of the book is an empirical argument that, in several important ways, pain is in fact amenable to language.
- The Wittgensteinian argument of chapter 2 can at best show that we must be able to communicate that we are in pain. But his project is to show that we can communicate what it is like to be in pain. He's not confusing the two in chapter 2. He wants to use the former as a wedge to open the door for the latter. But later on they sometimes seem to get run together in significant ways.
- His discussion of the language/metaphors of agency does a lot to support and build on Elaine Scarry's articulation of the concept (I profited a great deal from this part since the pain-agency connection is important in my own work). The discussions of the x-ray and mirror metaphors/language are much weaker. Indeed, I'm not convinced that these can't be folded into the agency metaphor. [Unlike the others, this concern has significant philosophical consequences for our understanding of pain]
- I'm probably being overly picky --but, hey, that's what analytic philosophers are for-- but his project is about language (hence the title and the claim to be constructing a 'rhetoric'). I usually think of language as propositional. His discussions using art to express pain thus seem incongruous. This is probably innocuous. At most it's a concern about whether the thesis should be framed in terms of language or more broadly in terms of our ability to meaningfully communicate. Though I sometimes think that there may be something lurking here that's related to the more substantive questions about whether the x-ray and mirror metaphors are really separate from the agency metaphors.
- I'm betting that analytic philosophers of language who work on metaphor will find a great deal to disagree with in some of his arguments. Though I myself don't know enough about these issues to have more than hazy suspicions at various points.
Like I said, I'm not entirely sure what I think about these and other points. But I've certainly profited from thinking about them. And in any event, none of them undermine the practical import of the book or the philosophical suggestiveness of the overall picture. Indeed, his subtle discussions of pain language’s structure do not require the conceptually strong thesis that the experience of pain is necessarily expressible. By weaving together art, literature, personal experience, and patient testimony, he has demonstrated that many aspects of many pain experiences can, to a practically useful degree, be meaningfully shared.
A critique and new version of the Wong-Baker Pain Faces Scale
We're all familiar with the Wong-Baker Pain Faces Scale.

But as our Hyperbolic critic notes, this is easily misunderstood. For example, she interprets it as
0: Haha! I'm not wearing any pants!
2: Awesome! Someone just offered me a free hot dog!
4: Huh. I never knew that about giraffes.
6: I'm sorry about your cat, but can we talk about something else now? I'm bored.
8: The ice cream I bought barely has any cookie dough chunks in it. This is not what I expected and I am disappointed.
10: You hurt my feelings and now I'm crying!
Thus she has come up with a better scale:

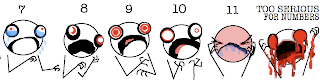
Which she interprets as:
0: Hi. I am not experiencing any pain at all. I don't know why I'm even here.
1: I am completely unsure whether I am experiencing pain or itching or maybe I just have a bad taste in my mouth.
2: I probably just need a Band Aid.
3: This is distressing. I don't want this to be happening to me at all.
4: My pain is not fucking around.
5: Why is this happening to me??
6: Ow. Okay, my pain is super legit now.
7: I see Jesus coming for me and I'm scared.
8: I am experiencing a disturbing amount of pain. I might actually be dying. Please help.
9: I am almost definitely dying.
10: I am actively being mauled by a bear.
11: Blood is going to explode out of my face at any moment.
Too Serious For Numbers: You probably have ebola. It appears that you may also be suffering from Stigmata and/or pinkeye.
I expect to see this written up in Pain shortly.
